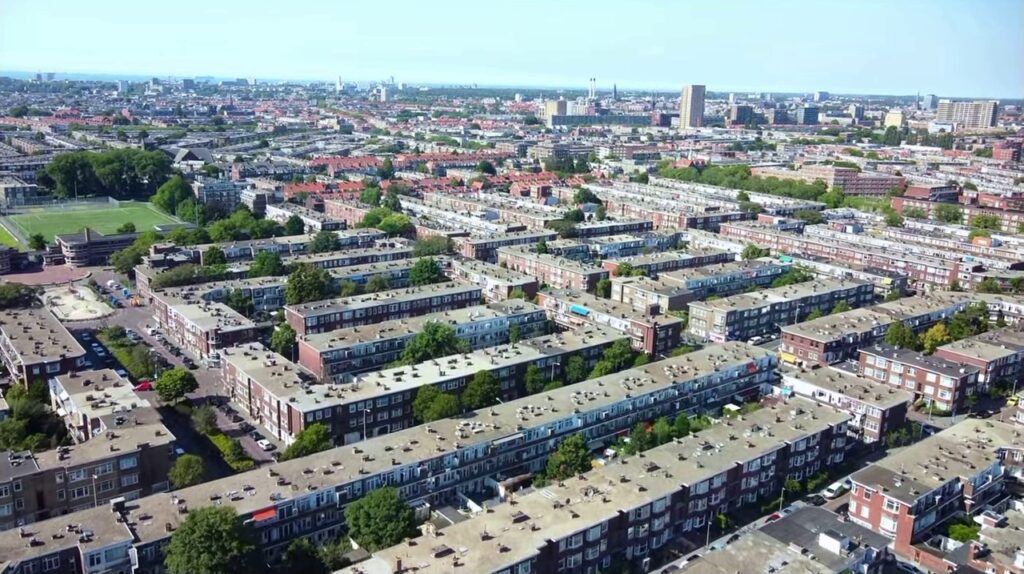
Urban regeneration process called gentrification transforms a community from a lower-income region to an affluent one, frequently displacing long-term residents in the process. Particularly in big cities like Amsterdam, Rotterdam, and Utrecht, gentrification has grown to be a significant problem in the Netherlands.
Gentrification
In the Netherlands, urban housing shortages and rising demand for homes are the main factors causing gentrification. Factors including population growth, immigration, and the expansion of the tech and creative industries have all contributed to this demand.
Netherlands
The removal of low-income residents from their houses and neighborhoods is one of the main effects of gentrification in the Netherlands. Rising rents and property values as a result of gentrification can drive long time people out of their communities. Due to the loss of the diversity and vibrancy that made these communities special, this can have a substantial effect on their social fabric.
Construction
The Netherlands government has developed regulations to encourage the construction of affordable housing and to protect renters from unjustified rent hikes and evictions in order to combat the issue of gentrification. Community groups and activists have also been fighting for the rights of low-income inhabitants and bringing attention to the negative effects of gentrification.
Building
In general, gentrification is a complicated problem that must be addressed in a multidimensional manner. Urban renewal has the potential to significantly improve neighborhoods, but it is crucial to make sure that all residents—not just those who can afford increased rents and property values—benefit from these changes.